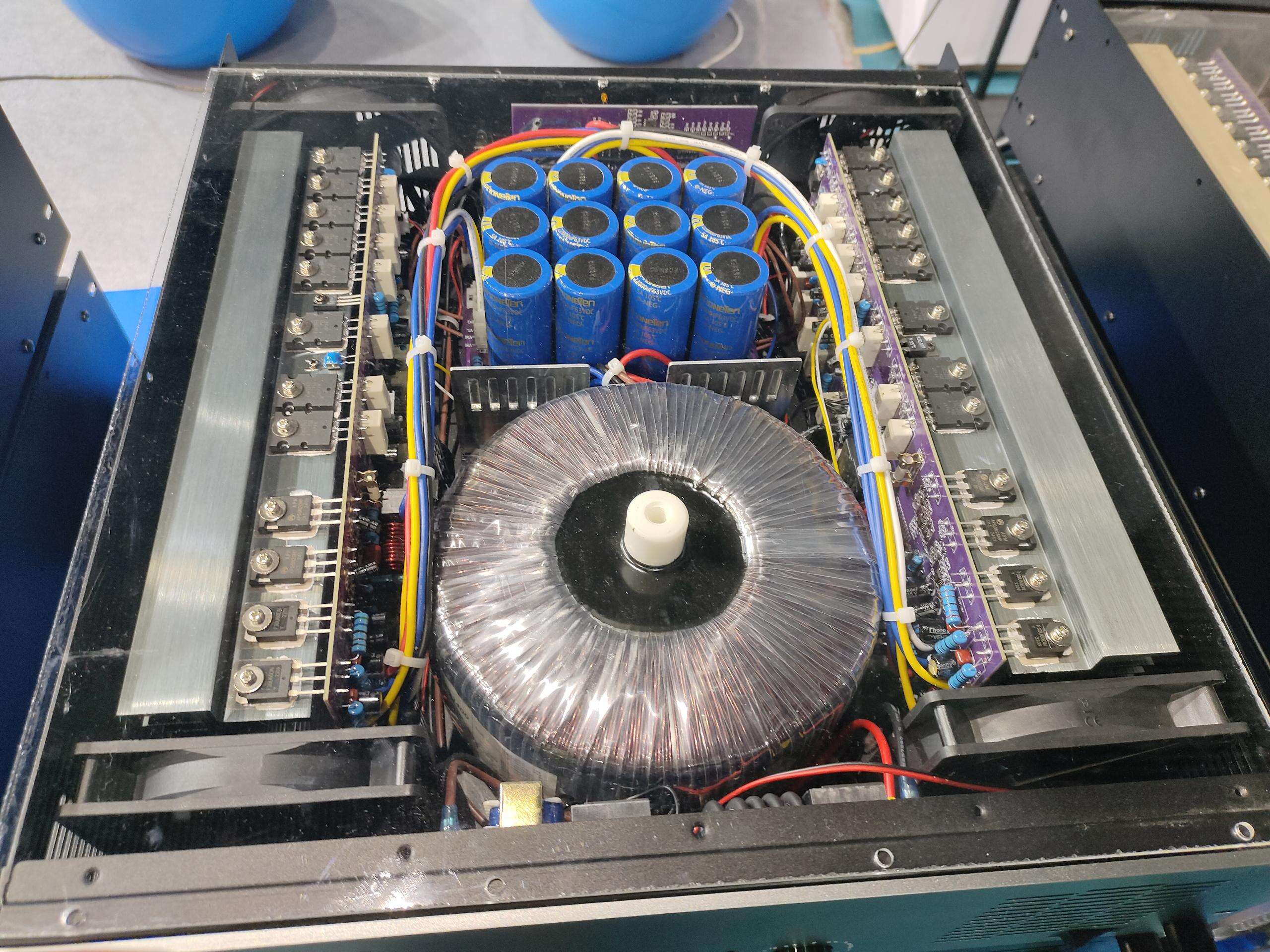
In the world of audio engineering and electronic amplification, achieving precise impedance matching stands as one of the most critical factors determining system performance. Amplifier transformers serve as the cornerstone technology that bridges the gap between amplifier circuits and output loads, ensuring maximum power transfer while minimizing signal distortion. These specialized components have evolved significantly over decades, incorporating advanced materials and design methodologies to meet the demanding requirements of modern audio applications. Understanding how amplifier transformers function in impedance matching reveals the sophisticated engineering principles that enable high-fidelity sound reproduction across various professional and consumer audio systems.
Understanding Impedance Matching Fundamentals
Basic Principles of Impedance Theory
Impedance matching represents the electrical engineering concept of optimizing the transfer of electrical energy between different circuit components. When amplifier transformers connect amplification stages to speaker loads, they must account for the complex impedance characteristics that vary with frequency. The fundamental principle operates on the maximum power transfer theorem, which states that maximum power flows from source to load when their impedances are properly matched. This matching process involves both resistive and reactive components, creating a complex mathematical relationship that amplifier transformers must navigate with precision.
The impedance matching process requires careful consideration of the transformer's turns ratio, which directly affects the impedance transformation between primary and secondary windings. Professional audio applications demand extremely tight tolerance control, as even small impedance mismatches can result in significant power losses and frequency response irregularities. Modern amplifier transformers incorporate sophisticated core materials and winding techniques to achieve impedance matching accuracy within fractions of a percent across the entire audio spectrum.
Impact of Impedance Mismatches
When impedance matching fails to meet design specifications, the consequences extend far beyond simple power losses. Amplifier transformers operating with mismatched impedances generate unwanted reflections that create standing wave patterns within the circuit topology. These reflections manifest as frequency response anomalies, phase shifts, and increased distortion levels that degrade overall system performance. The resulting signal degradation becomes particularly problematic in high-end audio applications where listeners expect pristine sound reproduction without artifacts.
Furthermore, impedance mismatches force amplifier transformers to operate outside their optimal design parameters, potentially leading to increased heating, reduced efficiency, and accelerated component aging. The thermal stress generated by improper impedance matching can cause permanent changes to transformer characteristics, creating a cascading effect that worsens system performance over time. Professional audio engineers recognize these risks and implement comprehensive impedance matching strategies to preserve long-term system reliability and performance consistency.

Transformer Design Elements for Impedance Control
Core Material Selection and Properties
The core material selection process significantly influences how effectively amplifier transformers achieve accurate impedance matching across varying operating conditions. High-grade silicon steel laminations provide excellent magnetic permeability while minimizing eddy current losses that could affect impedance characteristics. Advanced core materials such as amorphous metals and nanocrystalline alloys offer superior frequency response and reduced core losses, enabling more precise impedance matching throughout the audio spectrum. The magnetic properties of these materials remain stable across temperature variations, ensuring consistent impedance matching performance regardless of operating environment.
Grain-oriented electrical steel represents another significant advancement in core material technology for amplifier transformers. This specialized steel exhibits directional magnetic properties that enhance flux density capabilities while reducing hysteresis losses. The improved magnetic characteristics translate directly into more predictable impedance behavior, allowing designers to achieve tighter impedance matching tolerances. Manufacturing processes for these advanced core materials involve precise control of crystalline structure and surface treatments that optimize magnetic performance for audio frequency applications.
Winding Configuration and Turn Ratio Optimization
The winding configuration design process determines how effectively amplifier transformers can achieve precise impedance matching between different circuit sections. Multi-layer winding techniques enable designers to create complex impedance transformation ratios while maintaining excellent frequency response characteristics. The physical arrangement of primary and secondary windings affects leakage inductance values, which directly influence impedance matching accuracy at higher frequencies. Professional-grade amplifier transformers often employ interleaved winding patterns that minimize leakage inductance and improve impedance matching consistency across the audio bandwidth.
Turn ratio calculations require sophisticated mathematical modeling that accounts for distributed capacitance, leakage inductance, and core losses under varying load conditions. Modern design software enables engineers to optimize winding configurations for specific impedance matching requirements while considering manufacturing tolerances and material variations. The resulting designs achieve impedance matching accuracy levels that were previously unattainable with conventional design approaches, enabling superior audio system performance in professional applications.
Toroidal Transformer Advantages in Audio Applications
Magnetic Field Containment and Efficiency
Toroidal transformers offer significant advantages for amplifier applications due to their superior magnetic field containment properties that enhance impedance matching stability. The closed-loop magnetic path eliminates external magnetic fields that could interact with nearby components and affect impedance characteristics. This magnetic isolation ensures that impedance matching remains consistent even in densely packed electronic equipment where multiple transformers operate in close proximity. The reduced electromagnetic interference translates into cleaner signal paths and more accurate impedance matching throughout the audio frequency range.
Energy efficiency improvements in toroidal designs directly benefit impedance matching performance by reducing internal losses that could affect transformer characteristics. The continuous core structure minimizes air gaps that create magnetic reluctance variations, resulting in more linear impedance transformation behavior. Higher efficiency operation also reduces thermal stress on transformer materials, maintaining stable impedance characteristics over extended operating periods. These thermal stability improvements prove particularly valuable in professional audio applications where consistent performance remains critical during long operating sessions.
Mechanical Construction Benefits
The mechanical construction advantages of toroidal amplifier transformers contribute significantly to impedance matching precision through reduced vibration sensitivity and improved structural integrity. The symmetrical winding distribution around the toroidal core creates balanced mechanical forces that minimize microphonic effects during operation. This mechanical stability prevents small variations in winding geometry that could affect impedance characteristics, particularly at higher signal levels where transformer saturation begins to influence performance.
Compact form factor benefits enable designers to position toroidal transformers closer to circuit elements requiring impedance matching, reducing parasitic inductance and capacitance effects from interconnecting conductors. Shorter connection lengths preserve impedance matching accuracy by minimizing the influence of external factors on transformer performance. The reduced size and weight also facilitate better heat dissipation design, maintaining stable operating temperatures that preserve impedance matching consistency over time.
Frequency Response Considerations
Low Frequency Performance Optimization
Low frequency impedance matching presents unique challenges for amplifier transformers due to the relationship between core saturation and impedance characteristics at high signal levels. Primary inductance values must remain sufficiently high to maintain proper impedance matching at the lowest frequencies of interest, typically extending down to 20 Hz for full-range audio applications. Core material selection and physical size optimization enable transformers to achieve the necessary inductance levels while avoiding excessive size and cost penalties that would make practical implementation difficult.
The interaction between core saturation and impedance matching becomes particularly critical when amplifier transformers handle high-power, low-frequency signals typical of bass reproduction applications. Advanced core materials with higher saturation flux densities enable transformers to maintain linear impedance characteristics at higher signal levels before saturation effects begin to degrade matching accuracy. Careful magnetic circuit design ensures that impedance matching remains stable even under dynamic signal conditions where instantaneous power levels may exceed average operating conditions.
High Frequency Response Characteristics
High frequency impedance matching accuracy depends heavily on minimizing parasitic elements within amplifier transformers that create frequency-dependent impedance variations. Leakage inductance between primary and secondary windings acts as a series impedance that affects matching accuracy at higher frequencies. Advanced winding techniques such as bifilar and trifilar configurations reduce leakage inductance while maintaining proper impedance transformation ratios. The resulting frequency response improvements enable accurate impedance matching well beyond the traditional audio bandwidth limits.
Distributed capacitance between transformer windings creates parallel impedance paths that can significantly affect high frequency impedance matching performance. Specialized insulation materials and winding geometries minimize these capacitive effects while maintaining necessary electrical isolation between windings. The optimization process requires careful balance between conflicting requirements, as techniques that reduce one parasitic element may increase others. Successful high frequency impedance matching design demands comprehensive understanding of these interactions and their cumulative effects on transformer performance.
Practical Implementation Strategies
Load Matching Techniques
Effective load matching strategies for amplifier transformers require comprehensive analysis of both source and load impedance characteristics across the intended operating frequency range. Multi-tap transformers provide flexibility for matching various speaker impedances while maintaining optimal performance characteristics. The tap selection process must consider not only nominal impedance values but also the frequency-dependent variations typical of real-world speaker systems. Professional installations often employ impedance measurement equipment to verify matching accuracy and optimize system performance.
Dynamic load conditions present additional challenges for impedance matching accuracy, as speaker impedances vary significantly with frequency, temperature, and drive level. Amplifier transformers must maintain stable impedance transformation ratios despite these variations to preserve system performance. Advanced transformer designs incorporate compensation techniques that account for predictable load variations, improving overall matching accuracy under real-world operating conditions. These design refinements prove particularly valuable in high-performance audio systems where impedance matching accuracy directly affects sound quality.
System Integration Considerations
Successful system integration of amplifier transformers requires careful attention to grounding schemes, shielding arrangements, and mechanical mounting techniques that preserve impedance matching accuracy. Ground loop prevention measures ensure that impedance measurements remain accurate and repeatable across different installation environments. Proper shielding techniques prevent external electromagnetic fields from affecting transformer impedance characteristics, particularly important in installations with high-power transmitters or other sources of strong electromagnetic fields nearby.
Thermal management strategies significantly impact long-term impedance matching stability by maintaining consistent operating temperatures that preserve transformer material properties. Adequate ventilation and heat sinking prevent thermal drift in transformer characteristics that could affect impedance matching accuracy over time. Professional installations incorporate temperature monitoring systems that track transformer operating conditions and provide early warning of thermal conditions that might compromise performance. These proactive measures ensure sustained impedance matching accuracy throughout the system's operational lifetime.
FAQ
What factors determine the optimal impedance matching ratio for amplifier transformers?
The optimal impedance matching ratio depends on the source impedance of the amplifier output stage and the load impedance of the connected speakers or circuits. Amplifier transformers must provide impedance transformation that maximizes power transfer while maintaining frequency response linearity. Factors include the amplifier's output impedance characteristics, speaker nominal and frequency-dependent impedances, desired power levels, and bandwidth requirements. Professional applications often require custom impedance ratios calculated specifically for the intended system configuration to achieve optimal performance across all operating conditions.
How do core losses affect impedance matching accuracy in high-power applications?
Core losses in amplifier transformers create frequency-dependent resistance that appears in series with the ideal transformer impedance, affecting matching accuracy particularly at higher power levels. Hysteresis and eddy current losses increase with signal level and frequency, causing impedance characteristics to deviate from theoretical values. High-grade core materials minimize these losses through improved magnetic properties and lamination techniques. Proper core material selection and sizing ensure that losses remain acceptably low even at maximum power levels, preserving impedance matching accuracy throughout the operating range.
What measurement techniques verify impedance matching accuracy in installed systems?
Impedance matching verification requires specialized test equipment capable of measuring complex impedance across the audio frequency range. Vector network analyzers provide the most accurate measurements by determining both magnitude and phase relationships between voltage and current. Alternatively, impedance bridges and dedicated audio impedance meters offer sufficient accuracy for most practical applications. Measurements should be performed under actual operating conditions including proper loading and signal levels to account for nonlinear effects that might not appear during low-level testing.
How do environmental factors affect long-term impedance matching stability?
Environmental factors including temperature, humidity, and vibration can significantly impact impedance matching stability over time. Temperature variations affect core material properties and winding resistance, causing gradual changes in impedance characteristics. Humidity exposure may degrade insulation materials and affect distributed capacitance between windings. Mechanical vibration can cause gradual changes in winding geometry that alter leakage inductance values. Professional installations incorporate environmental protection measures and periodic calibration procedures to maintain impedance matching accuracy despite these environmental influences.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Impedance Matching Fundamentals
- Transformer Design Elements for Impedance Control
- Toroidal Transformer Advantages in Audio Applications
- Frequency Response Considerations
- Practical Implementation Strategies
-
FAQ
- What factors determine the optimal impedance matching ratio for amplifier transformers?
- How do core losses affect impedance matching accuracy in high-power applications?
- What measurement techniques verify impedance matching accuracy in installed systems?
- How do environmental factors affect long-term impedance matching stability?